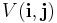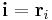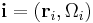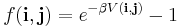Mayer f-function
The Mayer f-function is an auxiliary function that often appears in the series expansion of thermodynamic quantities related to classical many-particle systems.[1]
Definition
Consider a system of classical particles interacting through a pair-wise potential
where the bold labels 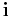 and
and  denote the continuous degrees of freedom associated with the particles, e.g.,
denote the continuous degrees of freedom associated with the particles, e.g.,
for spherically symmetric particles and
for rigid non-spherical particles where 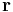 denotes position and
denotes position and 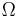 the orientation parametrized e.g. by Euler angles. The Mayer f-function is then defined as
the orientation parametrized e.g. by Euler angles. The Mayer f-function is then defined as
where 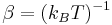 the inverse absolute temperature in units of (Temperature times the Boltzmann constant
the inverse absolute temperature in units of (Temperature times the Boltzmann constant 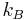 )-1 .
)-1 .
See also
Notes
- ^ Donald Allan McQuarrie, Statistical Mechanics (HarperCollins, 1976), page 228